Body butter and body lotion are both popular skincare products designed to nourish skin, so what makes them different?
Believe it or not, they’re not meant to be used interchangeably. While both aim to improve skin hydration levels, they differ significantly when it comes to texture, ingredients, moisturization levels, and who they’re most suited for.
Today, we here at Snif will be explaining the benefits of body butter and body lotion, what makes them different, and when it's best to use one or the other based on your environment, lifestyle, and skin’s unique needs.
What Is Body Butter?
Body butter is a rich, ultra-moisturizing product made with nourishing bases like shea butter, cocoa butter, or mango butter, along with hydrating ingredients such as jojoba oil, grapeseed oil, and vitamins.
Its primary function is to provide you with deep hydration, repair skin damage, lock in moisture, and create a protective barrier over your epidermis, which is the outermost layer of skin.
Although thicker than body lotion, body butter is applied similarly. For best results, massage a generous amount onto damp skin after a shower. This is when your pores are most open and can easily absorb products. Pay special attention to extra-dry areas like knees and elbows.
What Is Body Lotion?
Body lotion is a lightweight moisturizer made primarily with water for hydration and nourishing oils like coconut, almond, and olive oil. Its fast-absorbing formula is ideal for normal to slightly dry skin types, but isn’t always well suited for treating extremely dry skin.
Like body butter, body lotion intends to maintain moisture and support your overall skin health but with a thinner consistency suitable for daily use.
Body lotion is commonly applied in the morning, after a shower, or before bed, ensuring continuous hydration without leaving behind a greasy residue.
How Are Body Butters and Lotions Different?
Although body butters and body lotions serve a similar purpose, they have fundamental differences — including their composition, texture, and moisturization levels.
These distinctions affect how they feel on your skin and how intensely they hydrate. Each product is better at addressing certain needs and supporting different skin types.
Moisturization Level
Body butter and body lotion hydrate the skin at different intensities. Body butter gives you deep, long-lasting moisture and nourishment, making it a perfect choice for soothing very dry, rough skin that needs TLC.
On the other hand, body lotion gives you lightweight hydration, making it most suitable for daily use and maintaining generally soft, smooth skin.
Ingredients
When it comes to ingredients, body butters are rich in natural materials like shea butter, oils, and vitamins, offering deep nourishment. In contrast, body lotions have a high water content and contain added emollients, which help to lock in moisture by creating a protective film on the skin.
This barrier helps to keep skin smooth throughout the day by preventing water loss and maintaining healthy hydration levels.
Texture
The distinct ingredients in body butter and body lotion are what determine their textures. Body butters are thick, rich, and creamy thanks to their rich, nourishing ingredients.
Meanwhile, body lotions are generally lightweight and silky with a higher water content. Which of the two feels better on your skin is just a matter of personal preference!
When Is Body Butter Best?
Body butter is ideal for intensely dry skin, bringing you deep moisturization and repair with a thick, nourishing formula.
Dry Skin
Dry skin can be caused by a variety of factors. As we age, our skin naturally produces less oil and our skin becomes less moisturized — but conditions like eczema and psoriasis can also intensify dryness for people of all ages.
Lifestyle choices, like low water intake, can also contribute to dehydration. Thanks to its rich, hydrating composition, body butter is a great way to quench your dry skin.
Deep Moisturization and Repair
Your skin has a natural barrier called the stratum corneum, made of skin cells, natural oils, and lipids, which protects against pollutants and locks in moisture. When this barrier gets damaged, it can lose the oils necessary to maintain hydration… and the result is rough, flaky skin.
Using a thick, intensely nourishing body butter — especially one made with high-quality ingredients like organic oils and vitamins — can help replenish lost oils, nurturing your skin back to health.
When Is Body Lotion Best?
Body lotion is best for daily hydration to help maintain soft, healthy skin year-round with its lightweight formula.
Daily Use
As mentioned earlier, your skin has a natural protective barrier that helps to retain moisture and healthy hydration levels, but external factors can sometimes weaken it. Daily lotion use can help your skin maintain healthy moisture levels, preventing dryness, irritation, and flaking.
Everyday Skin Support
Even with healthy skin, environmental factors can negatively affect your hydration levels.
For example, in particularly sunny areas, environmental factors can damage your skin’s natural barrier, and in cold weather with low humidity, your natural moisture will be drawn away, leaving your skin dry. Support your skin daily by consistently applying body lotion.
Your Best Skin
To achieve healthier, more hydrated skin, we suggest using both body butter and lotion as needed! Incorporate body lotion into your daily routine to maintain moisture and softness, but keep body butter on hand for those days when you need a bit of extra nourishment — especially when treating dry patches.
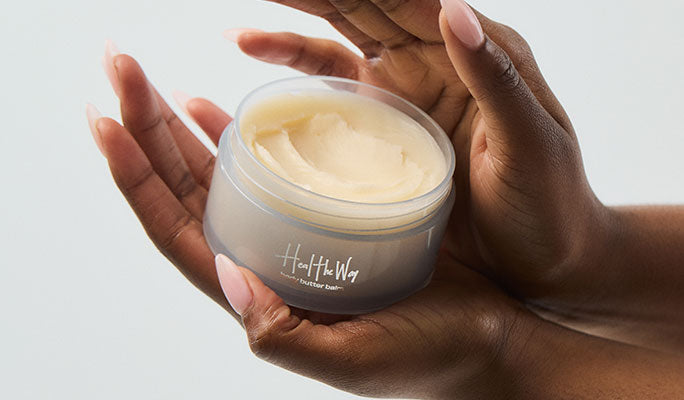
On the hunt for the perfect body butter? Try our Crumb Couture Body Butter Bar. As part of our decadent Crumb Couture Collection, this moisturizing bar makes your skin feel as good as it smells. Made with jojoba oil, grapeseed oil, vitamin E, and more, this product is expertly crafted to smell like croissant accord, wild berry jam, tonka bean, and toasted vanilla.
Deterred by the dairy in body butter? Not a problem, our products don’t have any! The Snif Body Butter Bar is vegan, non-toxic, and cruelty-free.
Sources:
Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis - StatPearls | NCBI Bookshelf
Emollients | National Eczema Society